Hiện thị UI lồng ghép vào trong trò chơi
Back to ezytankKhi phát triển các trò chơi 3D, việc hiển thị các thành phần UI (ví dụ như thanh máu, tên người chơi...) trực tiếp trong thế giới trò chơi giúp mang lại trải nghiệm tự nhiên hơn. Bài viết này mô tả cách EzyTank tích hợp một thanh máu tròn (HealthCircle) hiển thị phía dưới xe tăng sử dụng ECS của Unity. Dưới đây là các thành phần chính để thực hiện việc này:
HealthCircle prefab
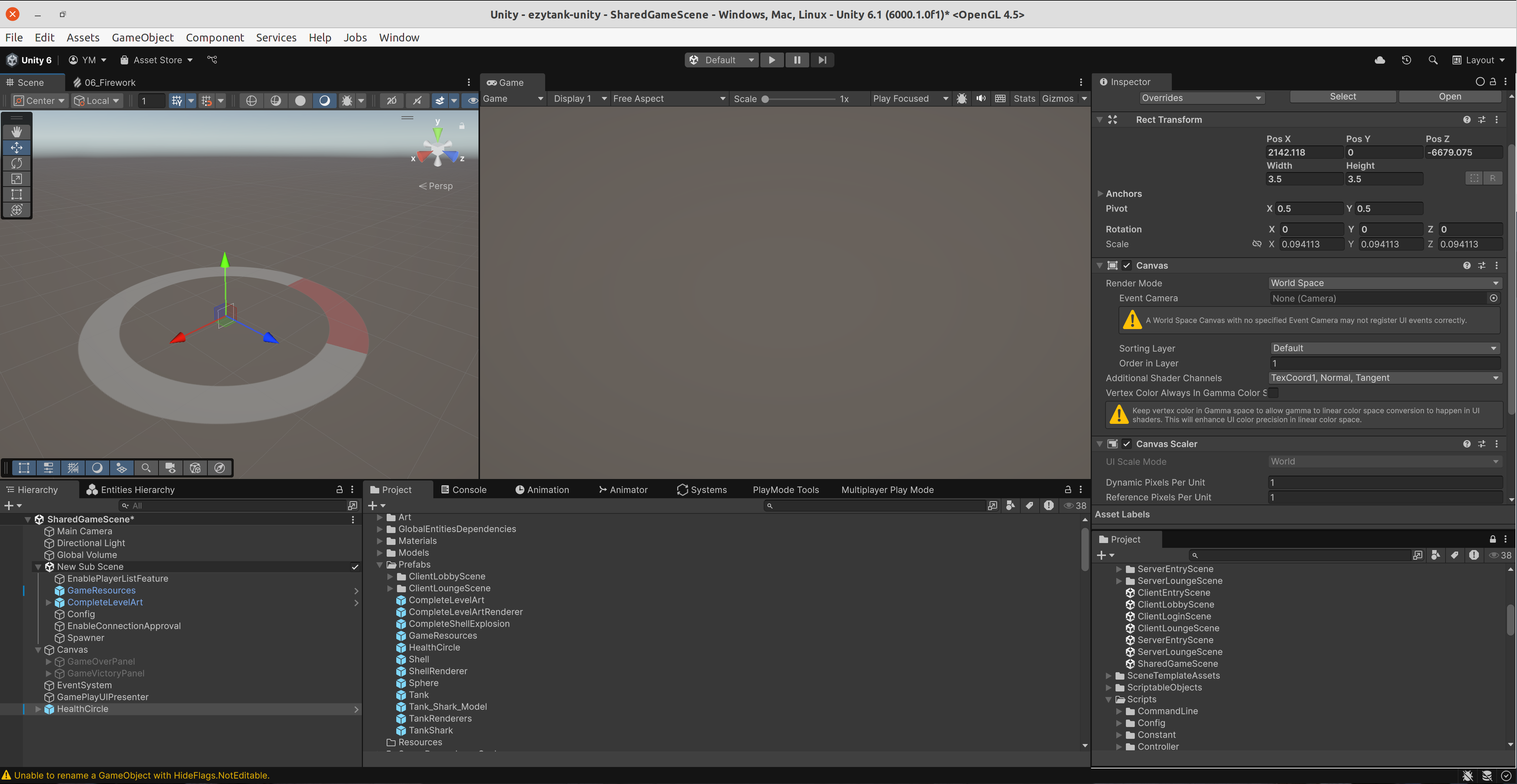
Việc chọn
Render Mode của canvas thành World Space là quan trọng nhất để có thể hiển thị các thành phần UI trong thế giới 3D.Nếu để mặc định là
Screen Space - Overlay hoặc Screen Space - Camera, UI sẽ được vẽ trực tiếp lên màn hình, không lồng ghép vào không gian 3D. Khi chọn World Space, canvas sẽ trở thành một đối tượng trong thế giới, có thể di chuyển, xoay và tỉ lệ hóa như bất kỳ GameObject nào, điều này cho phép chúng ta gắn nó lên các đối tượng trong trò chơi, chẳng hạn như xe tăng hoặc nhân vật.Trong prefab này, canvas chứa một GameObject con có component Slider dùng để hiển thị lượng máu còn lại. Việc cấu hình Slider cũng khá đơn giản và tương tự như trong các dự án Unity thông thường, chỉ khác là bây giờ nó sẽ được hiển thị trong không gian 3D thay vì giao diện 2D.
Đối tượng HealthCircleSpawner
Chúng ta có thể tìm thấy HealthCircleSpawner ở scene
SharedGameScene > subscene New Sub Scene như ở hình sau:
Đối tượng spawner này "sống" ở trong thế giới ECS, nên nó cần một authoring script
HealthCircleSpawnerAuthoring như sau để bake các thành phần:using Unity.Entities; using UnityEngine; namespace Youngmonkeys.EzyTank { public class HealthCircleSpawnerAuthoring : MonoBehaviour { public GameObject HealthBarPrefab; public float OpponentHeightOffset = 0.5f; public float PlayerTowardCameraOffset = 1.8f; public float PlayerHeightOffset = -1.5f; #if !UNITY_DISABLE_MANAGED_COMPONENTS class Baker : Baker<HealthCircleSpawnerAuthoring> { public override void Bake(HealthCircleSpawnerAuthoring authoring) { var entity = GetEntity(TransformUsageFlags.Dynamic); AddComponentObject( entity, new HealthCircleSpawner { HealthCirclePrefab = authoring.HealthBarPrefab, OpponentHeightOffset = authoring.OpponentHeightOffset, PlayerTowardCameraOffset = authoring.PlayerTowardCameraOffset, PlayerHeightOffset = authoring.PlayerHeightOffset, } ); } } #endif } #if !UNITY_DISABLE_MANAGED_COMPONENTS public class HealthCircleSpawner : IComponentData { public GameObject HealthCirclePrefab; public float OpponentHeightOffset; public float PlayerTowardCameraOffset; public float PlayerHeightOffset; } #endif }
HealthCircleSpawnerAuthoring cho phép gắn prefab HealthCircle vào hệ thống ECS. Các giá trị offset giúp định vị chính xác vị trí hiển thị của thanh máu so với xe tăng hoặc nhân vật.Hệ thống SpawnHealthCircleSystem trong ECS
Hệ thống này chịu trách nhiệm tạo (spawn) và hủy (despawn) các thanh máu tròn tương ứng với các thực thể có chứa thành phần Health.
using System; using Unity.Collections; using Unity.Entities; using UnityEngine; using UnityEngine.UI; using Object = UnityEngine.Object; namespace Youngmonkeys.EzyTank { #if !UNITY_DISABLE_MANAGED_COMPONENTS public class HealthUI : IComponentData, IDisposable, ICloneable { public Transform HealthCircle; public Slider HealthSlider; public float OpponentHeightOffset; public float PlayerHeightOffset; public float PlayerTowardCameraOffset; public void Dispose() { // As this is IDisposable, we can trigger the destruction of the HealthBar when this ghost entity is destroyed. if (HealthCircle != null) Object.Destroy(HealthCircle.gameObject); } public void SetActive(bool active) { if (HealthCircle != null) { HealthCircle.gameObject.SetActive(active); } } public object Clone() { if (HealthCircle == null || HealthCircle.gameObject == null) { return new HealthUI(); } var newHealthCircle = Object.Instantiate(HealthCircle.gameObject); var sliders = HealthCircle.gameObject.GetComponentsInChildren<Slider>(); return new HealthUI { HealthCircle = newHealthCircle.GetComponent<Transform>(), HealthSlider = sliders[0] }; } } [WorldSystemFilter(WorldSystemFilterFlags.ClientSimulation)] [UpdateInGroup(typeof(PresentationSystemGroup))] public partial struct SpawnHealthCircleSystem : ISystem { public void OnCreate(ref SystemState state) { state.RequireForUpdate<HealthCircleSpawner>(); state.RequireForUpdate<Health>(); } public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state) { EntityCommandBuffer ecb = new EntityCommandBuffer(Allocator.Temp); EntityQuery query = state.EntityManager.CreateEntityQuery(ComponentType.ReadOnly<HealthCircleSpawner>()); HealthCircleSpawner spawner = query.GetSingleton<HealthCircleSpawner>(); // Can't use job here because HealthCircleSpawner contains a managed object `HealthCirclePrefab` foreach (var (_, entity) in SystemAPI.Query<RefRO<Health>>().WithEntityAccess().WithNone<HealthUI>()) { GameObject gameObject = Object.Instantiate(spawner.HealthCirclePrefab); Slider[] sliders = gameObject.GetComponentsInChildren<Slider>(); ecb.AddComponent( entity, new HealthUI { HealthCircle = gameObject.transform, HealthSlider = sliders[0], OpponentHeightOffset = spawner.OpponentHeightOffset, PlayerTowardCameraOffset = spawner.PlayerTowardCameraOffset, PlayerHeightOffset = spawner.PlayerHeightOffset, } ); } ecb.Playback(state.EntityManager); } } [WorldSystemFilter(WorldSystemFilterFlags.ClientSimulation)] [UpdateInGroup(typeof(PresentationSystemGroup))] public partial struct DespawnHealthCircleSystem : ISystem { public void OnCreate(ref SystemState state) { state.RequireForUpdate<HealthUI>(); state.RequireForUpdate<DelayedDespawn>(); } public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state) { EntityCommandBuffer ecb = new EntityCommandBuffer(Allocator.Temp); foreach (var (delayedDespawn, healthUI) in SystemAPI.Query<RefRW<DelayedDespawn>, HealthUI>()) { if (delayedDespawn.ValueRO.hasHandledHealthUIDisabled == 0) { healthUI.SetActive(false); delayedDespawn.ValueRW.hasHandledHealthUIDisabled = 1; } } ecb.Playback(state.EntityManager); } } #endif }
Hệ thống trên hoạt động như sau:
-
SpawnHealthCircleSystem: Khi một thực thể có thành phầnHealthxuất hiện nhưng chưa có thành phầnHealthUI, hệ thống sẽ tạo mới một đối tượng của prefabHealthCirclevà gắn vào thực thể. -
DespawnHealthCircleSystem: Khi thực thể bị đánh dấu bởi thành phầnDelayedDespawn, UI sẽ bị tắt hoặc hủy đi tương ứng.
Vì sao HealthUI là class, không phải struct?
Trong Unity ECS, một component có thể là:
- IComponentData (struct): dữ liệu thuần (pure data), có thể được lưu trữ trong vùng nhớ native của ECS (cực kỳ hiệu quả và phù hợp với job).
- IComponentData (class): dữ liệu "được quản lý" (managed data), được lưu trong vùng nhớ quản lý của .NET (không thể dùng trong job).
HealthUI cần lưu trữ các thành phần như
Transform, Slider, và GameObject, tất cả đều là managed object trong Unity, không thể tồn tại trong vùng nhớ native của ECS. Vì vậy, nếu ta khai báo HealthUI là struct, Unity sẽ báo lỗi vì các đối tượng này không thể được sao chép hoặc lưu trong Burst hoặc JobComponentSystem.Tổng kết lại: Bằng cách sử dụng đối tượng Canvas ở chế độ
World Space và kết hợp với hệ thống ECS, ta có thể dễ dàng hiển thị các UI như thanh máu hoặc thông tin người chơi ngay trong không gian trò chơi. Cách làm này khá trực quan, mà vẫn đảm bảo hiệu năng và khả năng mở rộng khi phát triển game lớn.